Issue:
Stormwater Management
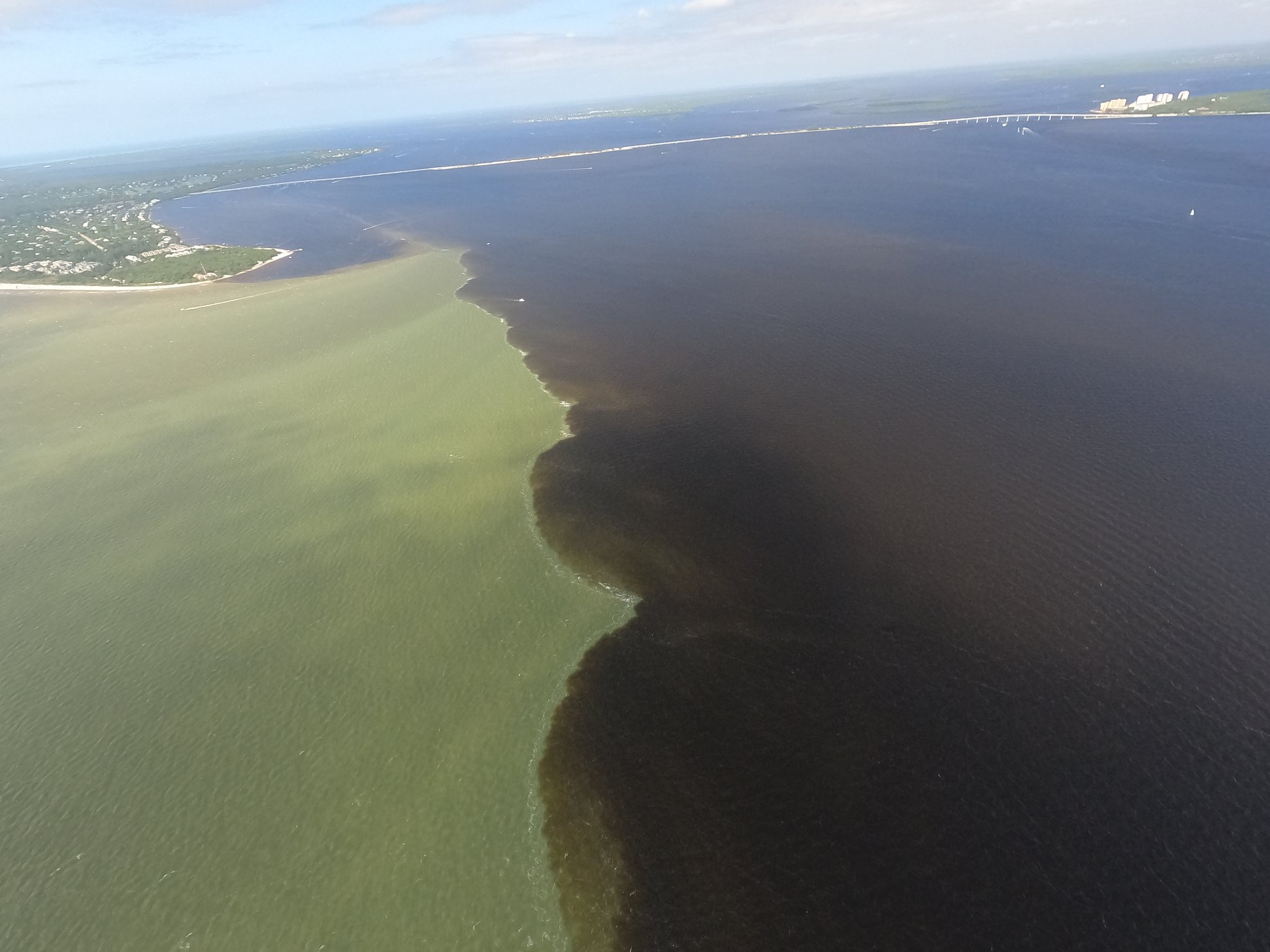

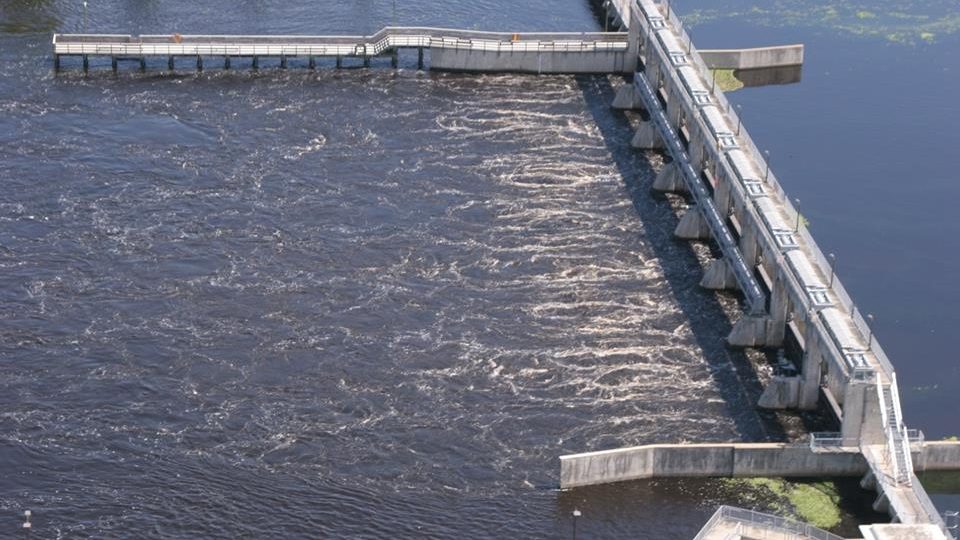
The effects of a rain event from the Caloosahatchee watershed, which often includes Lake Okeechobee discharges.
Stormwater & Nutrient Pollution
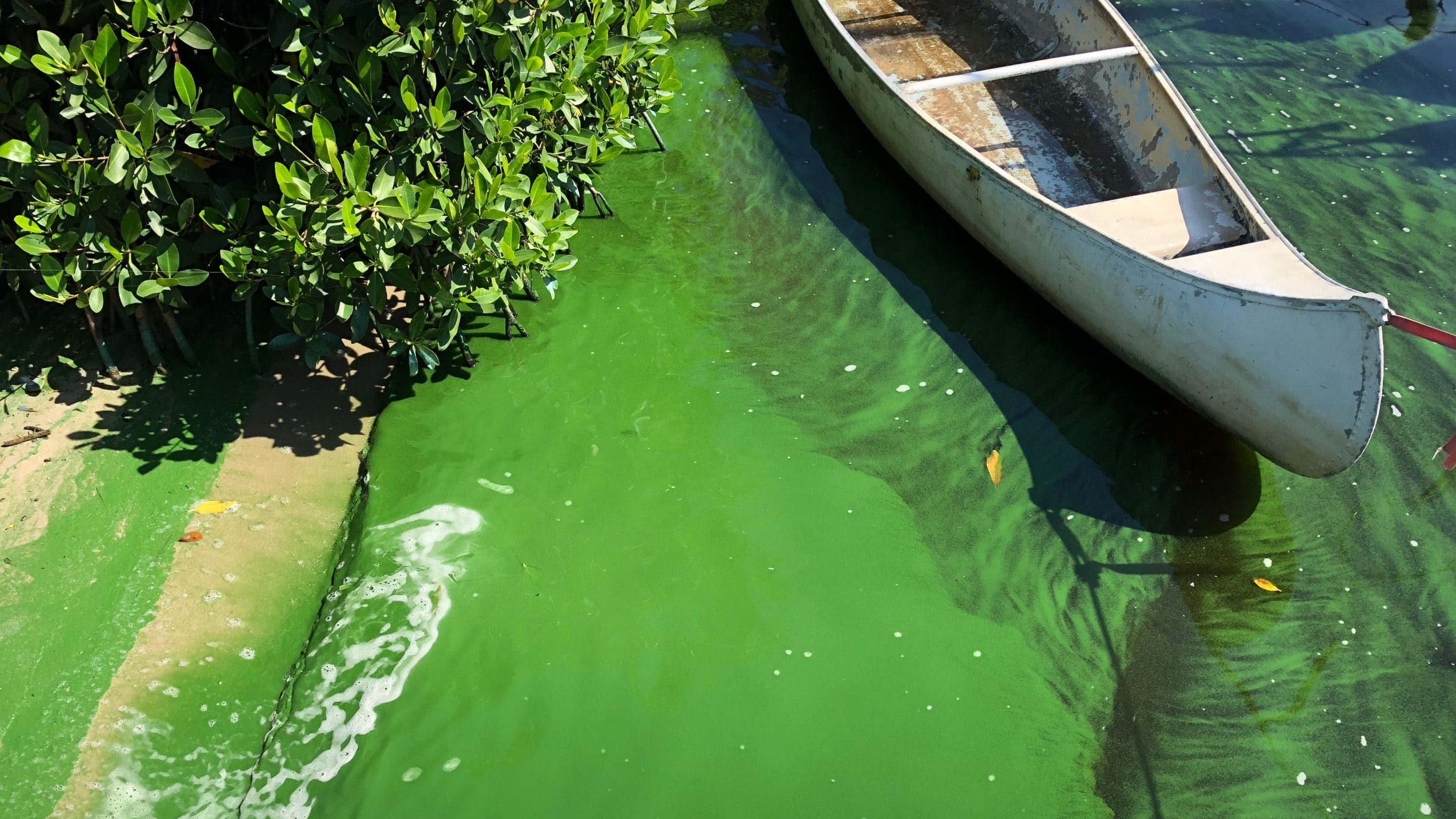
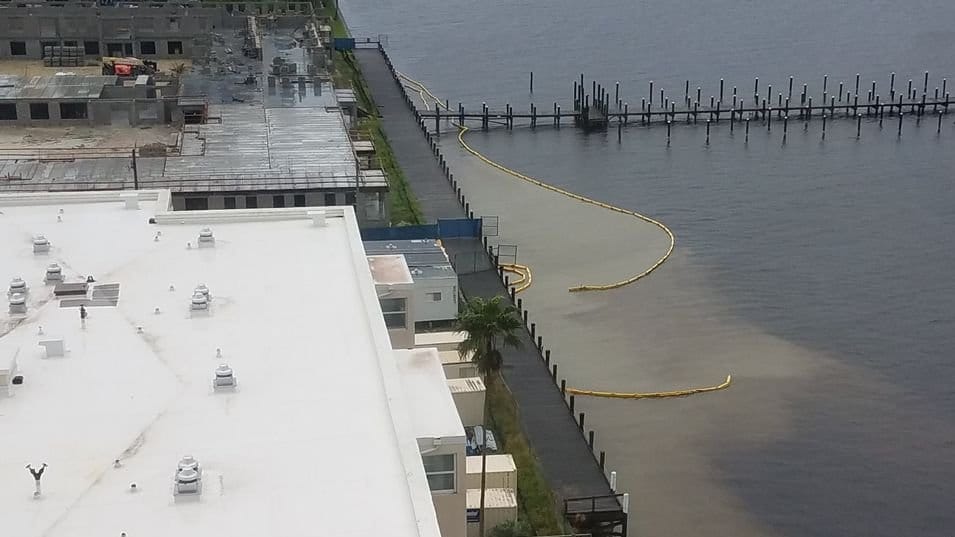
As the landscape is cleared for various uses, flood control measures typically create more water quality problems. Stormwater is engineered to run off into canals and waterways much quicker than in the natural systems which allowed for standing water and the filtering of pollutants by wetlands. Ditching, dredging and road building throughout Florida, has altered floways and accelerated runoff in many watersheds. This leads to downstream impacts to receiving waters from stormwater runoff, especially after large rain events.
Stormwater runoff is a dynamic vehicle that introduces many pollutants into our waters, including nitrogen, phosphorous, fecal bacteria, copper, mercury, plastics and more. Whether we’re talking about agricultural or residential uses, the development, fertilization, irrigation and flood control decisions we make on land have a lasting impact on water quality.
Stormwater management and oversight in Florida is a somewhat complex web of government and stakeholder involvement. Land owners, cities, counties and Community Development Districts (CDDs) are all responsible for compliance with the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) which the state’s Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP) is charged with overseeing. The state’s water management districts also play an important role in flood control projects and stormwater permitting on larger developments.
Many of our other priority issues are related to stormwater loading. For example, Lake Okeechobee discharges are driven by rainfall, carrying legacy nutrients and pollutants. Excess nutrient loading (pollution) of nitrogen and phosphorous are the primary fuel for harmful algal blooms.
When water on our landscape is not allowed time to percolate through the ground or a riparian buffer, it is often inadequately treated in stormwater treatment areas or drained directly into our waterways, taking contaminants with it.
Nutrients & Other Impairments
The Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP) oversees the assessment and verification of impairments to Florida waters. There are a variety of parameters that cause impairments, with the most common being for nutrients (nitrogen or phosphorous), dissolved oxygen, fecal indicator bacteria, turbidity, copper and mercury.
The process of classifying, grouping and assessing our waterbodies is quite laborious and complex. In our view, both the Basin Management Action Plans (BMAP) and accompanying Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDL) programs, created by the Florida legislature, are largely failing to protect and restore Florida’s impaired waters.
At Calusa Waterkeeper, we are doing our best to independently analyze the state’s stormwater rule-making process, vet local Municipal Separate Storm Sewer System (MS4) permits, identify possible NPDES stormwater violations and hold FDEP and polluters accountable to monitoring requirements and restoration plans.

By the Numbers
Water Quality Trends in SWFL
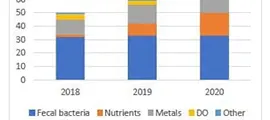
In 2021, Calusa Waterkeeper began a novel assessment of our local water quality trends using FDEP’s impairment data. This is a relatively comprehensive and unbiased way of determining local water quality trends.
This impairment assessment summary also represents a baseline that can be easily updated from annual FDEP comprehensive verified lists in association with evaluation criteria, such as population growth, that contribute to impairment as presented here. A relatively narrow initial period of record was chosen that would include the latest changes in assessment criteria for added inter-year comparability.
The summary may also provide a basis for evaluating restoration effectiveness by understanding net change in impairment through time.
Read More
Related News Stories
Stormwater
‘Look at the Water for Evidence’: Data Proves Florida Pollution Prevention not Working
Available water sampling data proves – for the first time – that Florida’s flagship program to reduce water pollution isn’t working. And that pollution is contaminating waterways and sparking toxic algal blooms in the St. Lucie and Caloosahatchee rivers.
Fixing the Flow
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers’ new plan to manage and distribute vast quantities of water coming into and going out of Lake Okeechobee — reducing flows both east and west unless the lake grows too full, and sending more water south — is a significant improvement over the old plan.
Guest Opinion: The Conservancy of SWFL: Staying the Course for the Public Good
In 2020, the Conservancy filed a lawsuit against Collier County for approving Rivergrass because the project blatantly flouted the county’s requirements for smart growth design, fiscal neutrality, and minimization of traffic impacts.
Conservancy’s Case Against Rivergrass Village Moves Forward with Outside Support
The Conservancy of Southwest Florida has filed documents supporting its appeal to overturn a court decision rejecting the group’s challenge to the development of Rivergrass, a village in eastern Collier County. Calusa Waterkeeper is one of over a dozen other groups filing briefs in support of the Conservancy.
Census Shows Threat to Wildlife & Water as Millions of Newcomers Feed Development
Florida’s soaring population is good for business, but there may be a hidden price: the health of the state’s life-sustaining environment. The Sunshine State added almost 3 million people in the past 10 years, swelling from 18.8 to 21.7 million and muscling into the No. 3 spot in the nation.
Report Shines Spotlight on Southwest Florida’s Water Issues
A state report shows trouble in Southwest Florida’s water. Scientists warn that areas of our water are polluted with nutrients and bacteria. While the findings are no surprise to those who sample and study our waterways, the unwanted attention could be a much-needed wake-up call.
Make a Donation
Get Notified
Priority Issues
Harmful Algal Blooms
Cyanobacteria & Red Tide
Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and Karenia brevis (red tide) have been making major impacts on Southwest Florida.
Lake Okeechobee Discharges
Revise System Operating Manual
The Caloosahatchee River often suffers from too much freshwater in the wet season, and not enough freshwater in the dry season.
Cape Coral Spreader Canals
Nutrient & Sediment Loading
The City of Cape Coral is working to remove large storm-water barriers to make recreational boating more convenient.
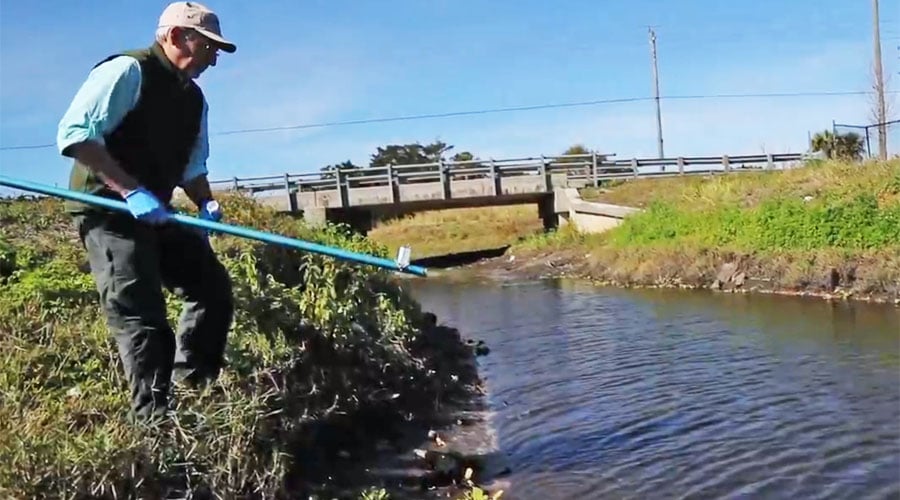
Bacteria Monitoring
Fecal Indicator Bacteria
Calusa Waterkeeper has been at the forefront of monitoring this Fort Myers tributary for fecal bacteria indicators.