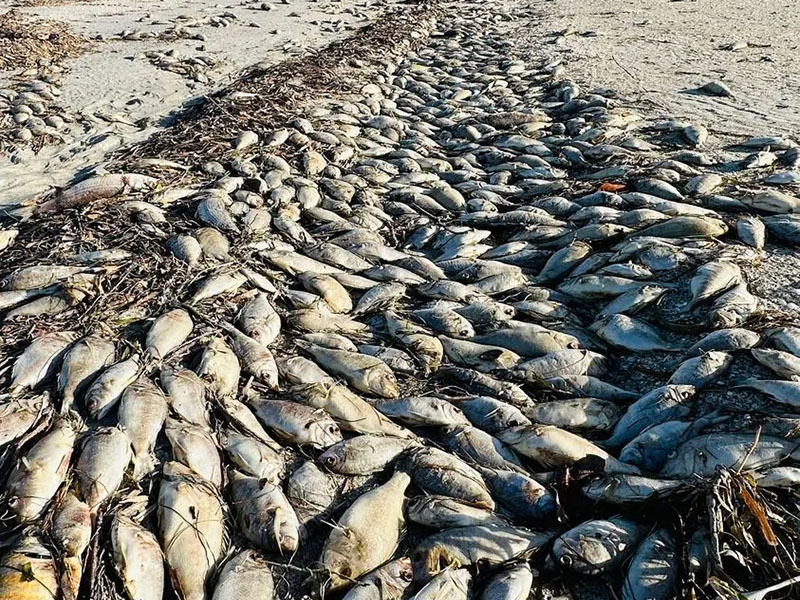
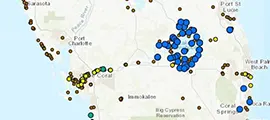
Scientists are saying a red tide bloom that’s lingered along the coast for a few weeks is now being fed by nutrients running off the landscape in the wake of Hurricane Ian.
Red tide (Karenia brevis) is a naturally occurring organism in the Gulf of Mexico that sometimes blooms to toxic levels.
But research shows that nutrients from farm fields, lawns and septic tanks fuel red tide blooms close to shore — making them more frequent, longer-lasting and more intense.
Calusa Waterkeeper John Cassani has been monitoring the bloom online.
“I’m hearing people aren’t seeing as many gamefish species as compared to (Hurricane) Irma (2017),” Cassani said. “It’s mostly foraging fish but most are decayed to the point you can’t determine the species.”
Hurricane Irma stirred up nutrients in the Lake Okeechobee/Caloosahatchee River system five years ago, and the following summer was virtually lost to a massive red tide and blue-green algae bloom in the river.
Lee County was part of a state of emergency for both blooms.
Some scientists have speculated that Hurricane Ian’s aftermath will cause similar conditions between now and the spring of 2024.
Continue Reading